The Inside Scoop on Penile Pumps
The use
of penile pumps may be an option if other medications cause side effects, don’t
work or aren’t safe for the individual. Penis pumps are a viable option if that
is the case. Studies show that 50-80% of men are satisfied
with the results of this form of treatment.
Penis pumps
are attractive to some individuals for a variety of reasons. Besides being
effective, penis pumps are also less risky than other treatments. Oral medications
pose the risk of several side effects, whereas penis pumps have lower risks of
side effects and complications. Furthermore, the overall cost of penis pumps as
a treatment for ED is lower than other forms, because there are minimal costs
after the initial purchase. Depending on the brand and type, most devices cost
anywhere between $300 to $500. Penis pumps may also be attractive to some
patients, because they are non-invasive and can be used with other medications,
such as oral medications.
Now
that penis pumps may seem like a feasible option, the next question is; how
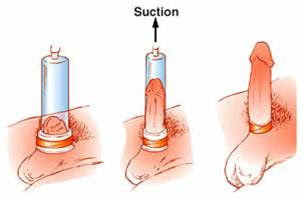
does one go about using one? A penis pump is composed of three
parts. It includes a clear, plastic tube, a pump attached to the tube and
powered by hand or battery, and a band, or constriction ring. The penis pump is
used with the following simple steps:
1. Place the clear, plastic tube over the penis. It
is important to get a good seal against the skin.
2.
Using either a hand pump or battery-powered
pump, create a vacuum inside the tube. This pulls blood into the penis.
3.
Once the erection has formed, slide the
constriction ring around the base of the penis. This keeps the blood inside the
penis and helps maintain the erection.
4.
Once the ring is in place, remove the vacuum
device.
According to Weill Cornell
Medical College, it takes an average of 10-20 minutes to achieve a full
erection. With the use of a penis pump, most men can keep an erection for about 30 minutes. The constriction ring should be removed once sexual relations are
complete. Constricting blood flow for too long may severely injury the penis.
Although penis pumps are generally
considered safe, it is important to take note of the potential associated side
effects. Increased bleeding may be caused in men who have sickle cell anemia,
take blood thinners, or have a condition interfering with clotting. Potential side
effects include numbness, bruising, pain, painful ejaculation or petechiae, or
the appearance of red dots caused by bleeding under the skin.
It is important to consult with a
doctor before using a penis pump to see if this route is an appropriate form of
treatment. Although the use of the penis pump won’t cure ED, it usually creates
an erection long enough to last for sexual relations.
 |
| Penile Vacuum Pump |
References:
"Erectile Dysfunction: Vacuum Constriction Devices." WebMD. WebMD, n.d. Web. 18 Mar. 2017.
<http://www.webmd.com/erectile-dysfunction/guide/vacuum-constriction-devices#2>.
Hospital, Ramayya Pramila Urology. "Erectile Dysfunction:Review." Ramayya Pramila Urology Hospital. N.p., 01 Jan. 1970. Web. 18 Mar. 2017. <http://drramayyas.blogspot.com/2010/03/erectile-dysfunctionreview.html>.
Medically Reviewed by George Krucik, MD, MBA on April 2, 2015 —
Written by Ann Pietrangelo. "What Is an Erectile Dysfunction Pump?" Healthline. N.p., 02 Apr. 2015. Web. 18 Mar. 2017.
<http://www.healthline.com/health/erectile-dysfunction/ed-pump#penis-enlargement8>.
"Penis Pump Results." Mayo Clinic. N.p., n.d. Web. 18 Mar. 2017.
<http://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/penis-pump/basics/results/prc-20013151>.
"What Are the Side Effects of Vacuum Constriction Devices? -
Penis Pump: Get the Facts on Vacuum Constriction Devices." MedicineNet. N.p., n.d. Web. 18 Mar. 2017.
<http://www.medicinenet.com/penis_prosthesis/page2.htm>.
Comments
Post a Comment